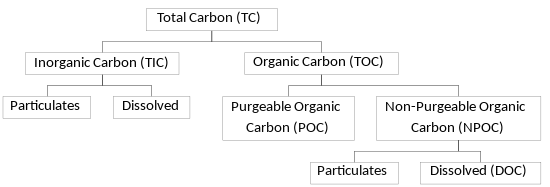
Any organic molecule you break down you will find carbon in. Total organic carbons (TOC) is the amount of carbon found in an organic compound and can be used a indicator of water purity.
Water also has inorganic carbon (IC) but IC is not included in the TOC measurement. (TOC = TC – IC)
How does does TOC affect me as a pathologist?
This is where the importance of consistently pure water becomes essential. In pathology impure water can give false readings of samples, incorrect analysis and diagnosis of medical conditions and contaminate your analyser.
As a guide the following levels of TOC are what are acceptable in type 1,2 and 3 water as according to the American society for Testing and Materials (ASTM)
Type 1 2: <50 ppb of TOCs
Type 3 : <200 ppb of TOCs
Water quality parameters for ISO grades.
| Perameter | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 |
| pH value at 25oC | — | — | 5.0-7.0 |
| Conductivity (μS/cm) at 25oC, max | 0.1 | 1.0 | 5.0 |
| Oxidisable matter Oxygen content (mg/l), max | — | 0.008 | 0.4 |
| Absorbance at 254 nm and 1 cm optical path length, absorbance units, max | 0.001 | 0.01 | — |
| Residue after evaporation on heating at 110oC (mg/kg), max | — | 1 | 2 |
| Silica (SiO2) content (mg/l), max | 0.01 | 0.02 | — |
American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM)
The ASTM uses D1193-06 and has four grades of water (see table below).
Water quality parameters for ASTM types.
| Perameter | Type I* | Type II** | Type III*** | Type IV |
| Conductivity (μS/cm) at 25oC, max | 0.056 | 1.0 | 0.25 | 5.0 |
| Resistivity (MΩ-cm) at 25oC, max | 18.0 | 1.0 | 4.0 | 0.2 |
| pH at 25oC | — | — | — | 5.0–8.0 |
| TOC (μg/l), max | 50 | 50 | 200 | No limit |
| Sodium (μg/l), max | 1 | 5 | 10 | 50 |
| Sodium (μg/l), max | 3 | 3 | 500 | No limit |
| Chloride (μg/l), max | 1 | 5 | 10 | 50 |
*Requires use of 0.2 μm membrane filter; **Prepared by distillation; ***Requires the use of 0.45 μm membrane filter.